A recent article from the UK focuses on whether bariatric surgery is effective as a treatment for type 1 diabetes mellitus. The article, titled “Bariatric Surgery in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review“ appeared October 9th in the journal Obesity Surgery.
Several new studies report that bariatric surgery can be effective for treatment of type 2 diabetes, however the role of bariatric surgery in type 1 diabetes is not clear. People with type 1 diabetes are increasingly obese and suffer from obesity related problems. Bariatric surgery in type 2 diabetes can lower blood pressure and reduce the amount of diabetes medication that is needed, therefore it could also provide similar benefits in people with type 1 diabetes.
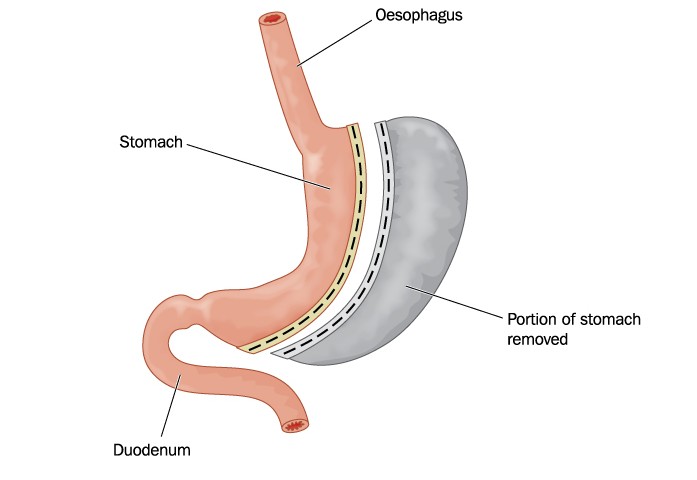
Different types of bariatric surgery exist. Sleeve gastrectomy is a surgical procedure that reduces the stomach to approximately 25% of its original size. This is accomplished by removing the more curved region of the stomach, which results in a stomach that looks like a sleeve. In gastric bypass surgery, the stomach is divided into a small upper region and a larger lower region, with a re-arranged piece of the small intestine connecting the two.
Led by Kamal K. Mahawar of Sunderland Royal Hospital in the UK, the authors of the recent report comprehensively reviewed English language scientific medical papers focusing how bariatric surgery impacts obese individuals with type 1 diabetes mellitus. They found overall that in obese people with type 1 diabetes bariatric surgery can induce significant weight loss and reduce co-existing conditions associated with diabetes. In their report, the study authors noted that “Though most patients also see a decline in total insulin requirement, [glucose] control remains difficult. Most of the patients reported in literature have undergone gastric bypass but data is insufficient to recommend any particular procedure.”
Overall, bariatric surgery may be beneficial for people with type 1 diabetes. However, additional studies are clearly needed to understand the impact of this type of surgery on type 1 diabetes and also to determine which type of bariatric surgery might provide the greatest benefit in this population of individuals.
The World Health Organization has estimated that the rate of obesity has more than doubled since 1980, with 39% of adults worldwide being overweight and 13% obese. Surgery can be very effective for reducing the health risks associated with obesity. The American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery notes that “Surgery results in significant weight loss and helps prevent, improve or resolve more than 40 obesity-related diseases or conditions including type 2 diabetes, heart disease, obstructive sleep apnea and certain cancers.”